PPP
TOYO PPP School
Outline (Outline and purpose/policies)
For International admissions, click here.
Brightening regional futures
with our Public-Private Partnership framework.
Now certified by the United Nations,
we will make a broad range of contributions to local administrations in Japan, Asia, and the world.
The Course of Public-Private Partnership of the Graduate School of Economics at Toyo University is aimed at working adults who study Public Private Partnerships.
Currently, many social issues are accumulating, such as aging populations with low birth rates, population decrease, aging infrastructure, and financial pressure on local governments. PPP is growing as an important policy tool to brighten the future of local regions.
Since its establishment in 2006, the Course of Public-Private Partnership has been cooperating with domestic and overseas local governments on implementing various projects. Within the Course of Public-Private Partnership there are three courses that bring together a diverse student body of local government personnel as well as those active in construction, real estate, finance, and overseas. Each student learns PPP in a manner that fits their individual needs and develops a stronger understanding.
In addition to the Course of Public-Private Partnership’s educational activities, the achievements of the Research Center for Public-Private Partnership and the Asia Public-Private Partnership Institute have received high evaluations. In 2015, the PPP education and research activities of Toyo University earned the certification of the United Nations’ Specialist Centre of Excellence on PPPs in Local Governments. Now, the school has become an intellectual hub, providing information on many research results in addition to collecting information on PPP from around the world.
PPP at Toyo University
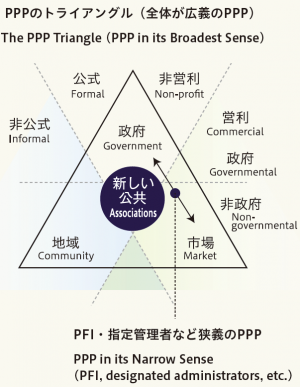
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) are an inclusive concept involving a method for project implementation with roles divided among the government, private industries, and citizens.
There is no legal definition of PPP, as is the case with PFI and designated administrators. Therefore, Toyo University’s Research Center for Public-Private Partnership has consulted with world organizations and created a two-stage definition.
Purpose/Policies
Appendix (1): Aim in Human Resource Development and Other Educational and Research Aims (Re: Art.2)
Graduate School of Economics
Aim in Human Resources Development and Other Educational and Research Aims
[Master’s Program]
(1) Objectives of Human Resources Development:
This Program aims to cultivate highly professional specialists who have the skills and knowledge required by the public and private sectors and can make optimal use of such capabilities to contribute to the social economy.
(2) Objectives of Education and Research: Knowledge and Skills Students Are Expected to Develop:
Students are expected to develop the ability to identify and resolve issues facing private companies and the local economy by utilizing a high level of comprehensive academic knowledge on and a deep understanding of economics.
Course of Public-Private Partnership, Graduate School of Economics
Aim in Human Resources Development and Other Educational and Research Aims
[Master’s Program]
(1) Objectives of Human Resources Development:
This Program aims to develop individuals who have a deep understanding of the behavioral principle of public and private entities and the abilities needed to promote cooperation between the two sectors, thereby contributing to the achievement of public purposes on a national or regional level.
(2) Objectives of Education and Research: Knowledge and Skills Students Are Expected to Develop:
Students are expected to develop basic knowledge on economics, finance, money and banking, management, and relevant laws and regulations, and acquire the capabilities required to play an active role in city planning, project development, or regional revitalization.
Appendix (2): Policies for Completion Certification, Degree Conferment, Curriculum Development and Implementation, and Admissions (Re: Art.3)
Course of Economics, Graduate School of Economics
1.Policy for Completion Certification, Degree Conferment (Diploma Policy)
[Master’s Program]
The Course of Economics will award a master’s degree to students who have acquired the following kinds of expertise and abilities, have satisfied the requirements, including the specified duration of study and number of credits, and have passed the examination of the Master’s thesis and the final examination:
(1) Comprehensive knowledge and understanding in the field of economics
(2) Excellent research capability in one’s field of specialization and the ability to write high-quality papers
(3) The ability to identify problems and resolve them, which is essential to play an active part in the real world
2. Policy for Curriculum Development and Implementation (Curriculum Policy)
[Master’s Program]
(1) Curriculum Development / Educational Content and Methods
To achieve the goals mentioned in the Diploma Policy, the Course of Economics will systematically develop a curriculum with an appropriate combination of “coursework” and “research work.” With open seminars, microeconomics, macroeconomics, statistics and econometrics as basic subjects, the curriculum of this Course features special lectures in various fields, including policy and economic history, global economics, industrial design, labor and social security, and environmental economics and policy. Lectures will be offered in small classes. Research work is provided under a responsible tutoring system with an academic supervisor and a co-supervisor at the core. Research advising on basic research methods, research themes, and paper writing will be provided in a closely supervised setting.
(2) Evaluation of Academic Grades
Academic grades will be evaluated objectively and strictly, using the following procedures and methods
① In coursework, students’ academic performance will be evaluated by instructors in charge in the manner that is stated in the syllabus of each course and in accordance with the evaluation criteria clarified in advance.
② In research work, students’ research achievements will be systematically assessed by research advising instructors and faculty members of the Course of Economics through thesis presentation sessions, etc., based on the research advising plan clarified in advance.
③ Master’s degree theses will be evaluated in accordance with the thesis review criteria and procedures clarified in advance.
3. Admissions Policy
[Master’s Program]
The Course of Public–Private Partnership will accept students with the following qualities and abilities by conducting a variety of examinations, including an essay exam, an interview and a screening of application materials, according to applicants’ characteristics.
(1) General Category: an individual, regardless of his/her field of specialization, who has his/her own view on local economies and communities (which is assessed by an essay exam) and who plans to make use of his/her specialized knowledge on public–private partnership (PPP) acquired in and of the network of personal connections built through this Course (which is assessed by an interview)
(2) Mature Student Category: an individual who has experience in a PPP-related field or may have a chance to be involved in such a field in the future, and who plans to make use of his/her specialized knowledge on public–private partnership (PPP) acquired in and of the network of personal connections built through this Course (which is assessed by an interview)
(3) International Student Category: an individual who has experience in a PPP-related field or may have a chance to be involved in such a field in the future in his/her home country, and who plans to make use of his/her specialized knowledge on public–private partnership (PPP) acquired in and of the network of personal connections built through this Course (which is assessed by an interview)
Appendix (3): Curriculums (Re: Art.4) Omission
Appendix (4): Number of Credits, etc. Required for Completion (Re: Art.5) Omission
Appendix (5): Courses to Be Taken and the Number of Credits to Be Earned forTeaching Certificates (Re: Art.7) Omission